Of the Following Which Best Describes the Sliding Filament Theory
Up to 24 cash back a. The sliding filament theory can be best explained as the following.

Illustration Of The Sliding Filament Hypothesis It Is Seen That When Download Scientific Diagram
Actin -actin monomers can bind with myosin actin has a myosin-binding site.

. Sliding theory states that. Tropomyosin QUESTION 4 According to the sliding filament model binding sites on actin open when creatine phosphate levels rise ATP levels rise acetylcholine levels rise calcium ion levels rise QUESTION 5 Which of the following best describes the diagram. Sliding filament theory is a model used to explain the mechanism by which muscles contract.
4The binding of ATP to the cross bridge which results in the cross bridge disconnecting from actin. Myosin bind to actin. 5The hydrolysis of ATP which leads to re-energizing.
1The influx of calcium triggering the exposure of the binding sites on actin. Can this particular myosin head bind to the actin filament forthe next. At a very basic level each muscle fibre is made up of smaller fibres called myofibrils.
Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction. This problem has been solved. Myosin rotates and wraps actin around it making the muscle shorter.
A A molecule of ATP binding to the myosin head. Presence of calcium ions in the cytosol trigger the exposure of binding sites on actin. These filaments slide in and out between each other to form a muscle contraction hence called the sliding filament theory.
A As they slide past each other actin filaments shorten but myosin filaments do not shorten. Biology 9th Edition Edit edition Solutions for Chapter 47 Problem 4U. See the answer See the answer See the answer done.
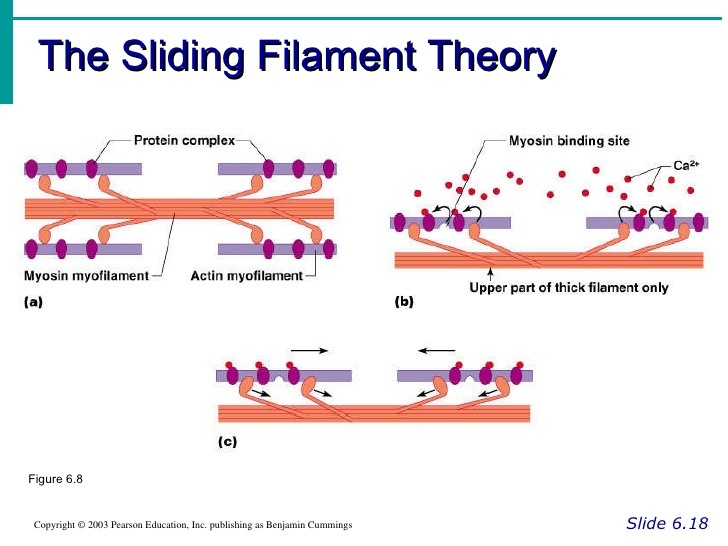
Sliding filament theory. The arrangement of actin and myosin myofilament within a sarcomere is crucial in the mechanism of muscle contraction. The interaction of these proteins is at the core of the sliding filament theory.
In 1954 two researchers Jean Hanson and Hugh Huxley from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology made a model for muscle tissue contraction which is known as the sliding filament theoryThis theory describes the way a muscle cell contracts or shortens as a whole by the sliding of thin filaments over thick filaments and pulling the Z discs. The diagram above shows part a myofibril called a sarcomere. Which of the following statements best describes the sliding filament mechanism of muscle contractiona.
The power stroke occurs. The sliding filament theory of muscle contraction says. - causes troponin to drag tropomyosin off cross bridge binding sites.
For a muscle to contract thick and thin filaments of sarcomeres do not shorten instead they slide by one another causing the sarcomere to shorten while the filaments remain the same length. A filament of myosin during cross bridge cycling. The sliding filament theory is a suggested mechanism of contraction of striated muscles actin and myosin filaments to be precise which overlap each other resulting in the shortening of the muscle fibre length.
This theory was proposed by HE Huxley and J. Which of the following best describes the diagram. Actin thin filaments combined with myosin thick filaments conduct cellular movements.
Muscular contraction Is the shortening of myofibrils in response to nervous stimulation and during this actin filament slides over myosin filament and links with them resulting in. One motor unit ОО An inactive actin filament The sliding filament theory O. B when myofilaments slide past each other shortening of actin filaments occur.
These contain even smaller structures called actin and myosin filaments. One motor unit An inactive actin filament The. The myosin then alters its configuration resulting in a stroke that pulls on the actin filament and causes it to slide across the myosin filament.
-cross bridges bind to actin. List the following steps in the order they would occur in a single cross bridge cycle. The mechanism of muscle contraction is explained by sliding filament model.
Which ONE of the following best describes the term sliding filament theory. C when myofilaments slide past each other shortening of myosin filaments occur. The contraction of skeletal muscle which is what makes movement possible occurs in three ways.
Actin and myosin filaments do not shorten but rather slide past each otherb. This mechanism is explained by the sliding filament theory. Actin and myosin filaments condense thus causing the filament to shorten which in turn shortens the muscle.
D actin and myosin filaments do not shorten they only slide past each other. Sliding Theory of Muscle Contraction. According to the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction the physical changes that occur in the sarcomere during contraction are a result of the thin filaments sliding past the thick filaments resulting in shortening of all the sarcomeres in a myofibril.
A actin and myosin filaments shorten and slide past each other. Actin and myosin filaments shorten and slide past each otherc. Up to 10 cash back The sliding filament theory describes the mechanism that allows muscles to contract.
2The binding of myosin to actin. Cross bridges on myosin pull on actin power stroke - actin filaments slide to middle of sarcomere. One motor unit ОО An inactive actin filament The sliding filament theory O.
Myosin can only bind to a binding site that is at the tip of a helix in the actin filament like the one in phase 1 of the model. 1 The release of acetylcholine along the motor neurons stimulating muscle contraction 2 Thick and thin filaments slide past one another to form muscle contractions 3 A neurotransmitter sends an impulse from one filament to the other enabling the muscle to lengthen thus creating. B As they slide past each other myosin filaments.
After the power stroke pulling phase and detachment is the myosin head lined up with a binding site at the tip of the filament. Calcium ions bind to troponin. ATP binds to the cross.
The sliding filament theory is a suggested mechanism of contraction of striated muscles actin and myosin filaments to be precise which overlap each other resulting in the shortening of the muscle fibre length. For a muscle contraction to take place there must be a stimulation first to form an impulse action potential from a neuron that connects to the muscle. The sarcoplasmic reticulum stimulated to release calcium ions.
The individual motor neuron plus and. B The hydrolysis of an ADP molecule on the actin filament. Actin thin filaments combined with myosin thick filaments conduct cellular movements.
Sliding filament theory may be used to describe how the muscles in the arm perform a bicep curl. In the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction what initiates the detachment of the myosin head from the binding site on the actin filament. Friction is reduced between thin and thick filaments causing the thick filaments to move inside.
Which of the following statements best describes the sliding filament mechanism of muscle contraction. The overall process shortens the sarcomere. According to this theory myosin a motor protein binds to actin.
According to the sliding filament theory when a muscle cell contracts the thin filaments slide past the thick filaments and the sarcomere shortens. Concentric muscle contraction involves the shortening of muscle fibers. A filament of myosin during cross bridge cycling.
3The power stroke of the cross bridge that causes the sliding of the thin filaments.
Sliding Filament Theory Biology Quizizz

Sliding Filament Theory Biology Quizizz

Sliding Filament Theory Diagram To Label Diagram Quizlet

Sliding Filament Theory Muscle Contraction 6 Steps D Diagram Quizlet
Comments
Post a Comment